Hangzhou archaeological digs rate among Zhejiang's top 10 finds
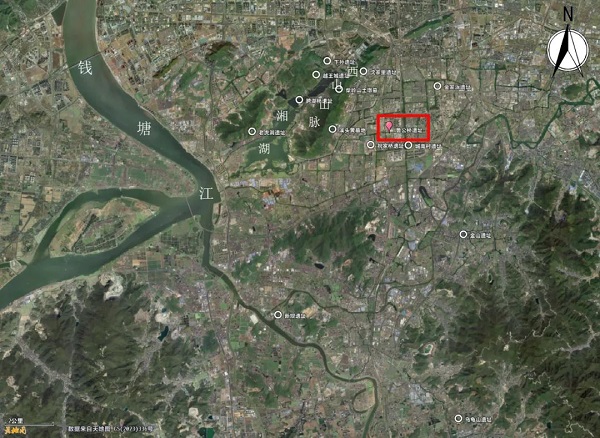
A satellite view of the Lugongqiao Site in Xiaoshan district. [Photo/WeChat account: zjfabu]
Two archaeological sites in Hangzhou – capital city of East China's Zhejiang province – were recently named among the region's top 10 archaeological discoveries of 2024.
The two finds are the Lugongqiao Site in the city's Xiaoshan district and the Yijin City Wall Site in Lin'an district.
The Lugongqiao Site is believed to hold cultural strata stretching from the Liangzhu period (3300–2300 BC) to the Ming and Qing dynasties (1368-1911).
Excavations from 2021 to 2024 have uncovered over 260 relics, including pits, tombs and wells, along with 3,000 artifacts such as pottery, jade and stone tools.
The site is deemed to provide crucial insights into settlement evolution in the Xiaoshao Plain and also insights into cultural exchanges between the Taihu Lake region and the surrounding areas.
For its part, the Yijin City Wall Site marks the location of the first city built by Qian Liu, the founding king of Wuyue, in the late Tang dynasty (618-907).
Recent excavations are said to have revealed remnants of the eastern city wall, drainage systems and architectural features. Notable finds have included porcelain, bricks with inscriptions and decorative elements including lotus-patterned tiles. The site reportedly offers invaluable information about Wuyue Kingdom's urban planning and defensive strategies.
Meanwhile, several other Hangzhou sites have also received recognition – highlighting the city's rich archaeological heritage and ongoing contributions to historical research.

A bird's-eye view of the Yijin City Wall Site in Lin'an district. [Photo/WeChat account: zjfabu]
-
Visionary Pathway - Hangzhou Playbook
July 15, 2025



